The 4 C’s of a Diamond

COLOUR
The less color, the higher the grade. Even the slightest hint can make a dramatic difference in value. The scale starts all the way down at ‘Z’ although we rarely see below a ‘K’. a diamond below a K will show heavy grey, yellow or brown colours. The highest colour is a D, meaning an absolute lack of colour in the diamond. Just like clarity the size of the diamond matters when considering its colour.

CARAT WEIGHT
Rarity means larger diamonds of the same quality are worth more per carat. This rarity goes up exponentially, meaning a 2 carat diamond is not twice as rare as a 1 carat diamond, but as much as 10 times rarer.
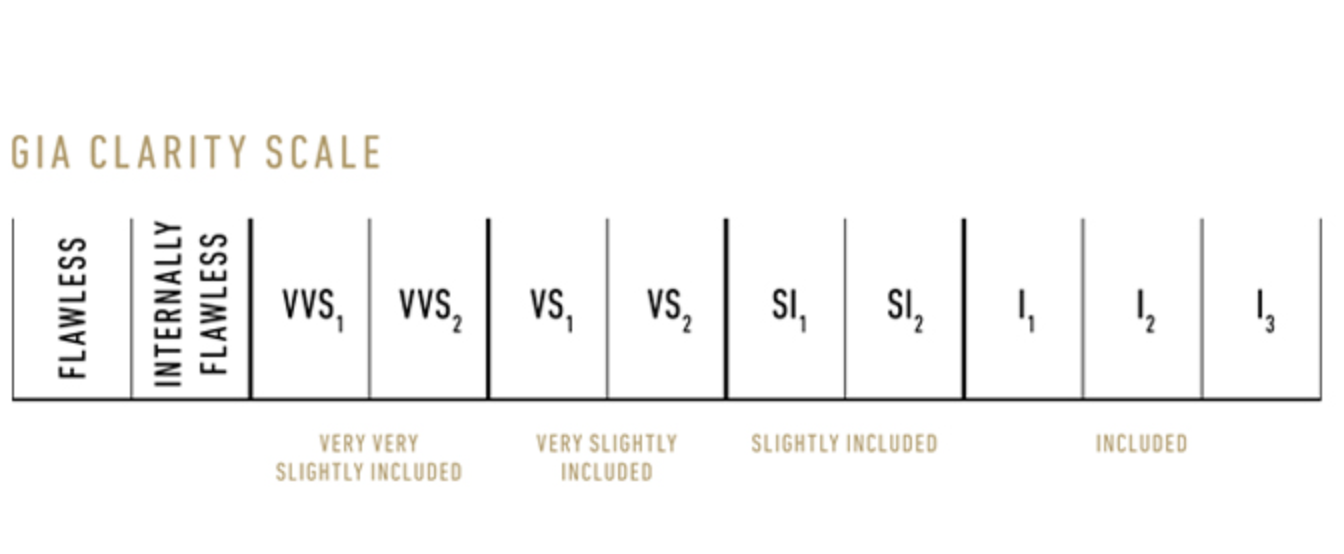
Clarity
Clarity grades assess the number, size and position of inclusions and blemishes. The scale starts at FL which stands for flawless. The scale ends at I3, meaning ‘included 3’. This is the most included a diamond can be. The size of diamonds greatly affects how important the clarity is to an individual stone. A larger stone will need a higher clarity than a small stone, as the inclusions are less visible.
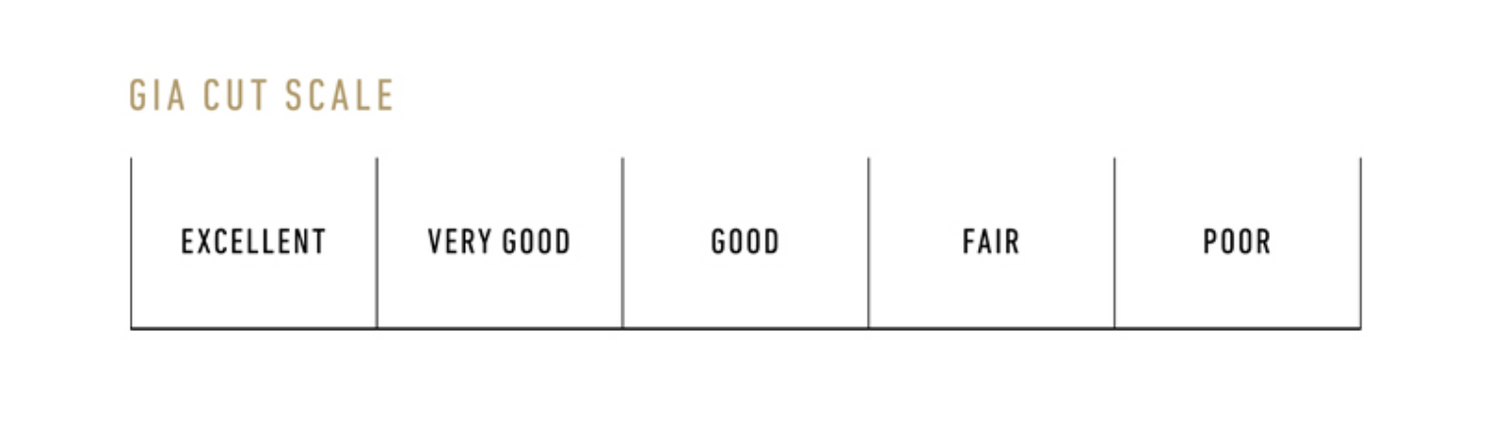
Cut
Cut (proportions, symmetry, and polish) is a measure of how a diamond’s facets interact with light.
